The effects of particle clustering on hindered settling in high-concentration particle suspensions
Abstract
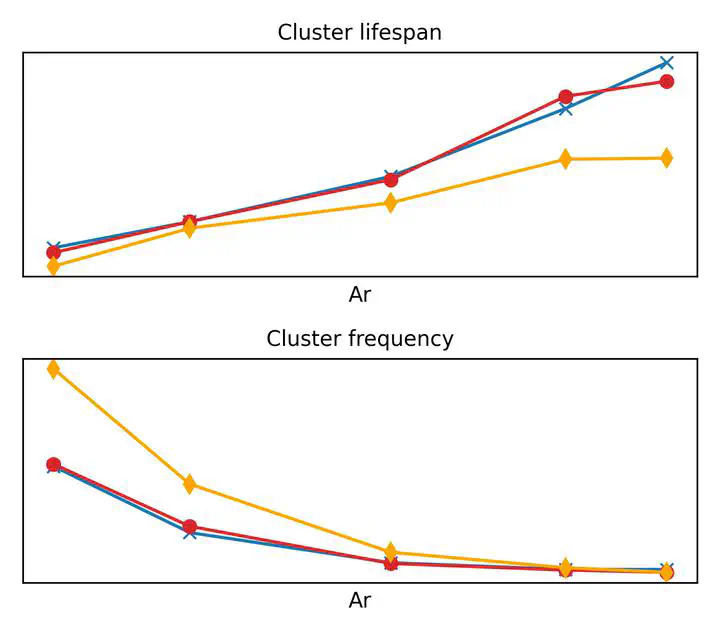
We study the effects of Archimedes number Ar and volume fraction $\phi$ in three-dimensional, high concentration and monodispersed particle suspensions. Simulations were conducted using the immersed boundary method with direct forcing for triply periodic cases and with Ar=21−23600 and $\phi=0.22−0.43$. We find that cluster formation is strongly dependent on the Archimedes number but weakly dependent on the volume fraction for concentrated suspensions. Particles in low Ar cases are characterized by less frequent but long-lived clusters, resulting in higher hindered settling, while high Ar cases consist of more frequent but short-lived clusters, leading to reduced hindered settling. By quantifying the effects of collisions on the hydrodynamic fluctuations, we show that the lifespan of clusters for the low Ar cases is longer because particles are subject to appreciable wake interactions without collisions. On the other hand, clusters for high Ar cases are broken before being subject to appreciable wake interactions due to frequent collisions, leading to a shorter cluster lifespan. The results imply that there exists an Ar for particles in fluidized bed reactors that can reduce short circuiting due to clustering and enhance performance by maximizing flow–particle interactions. This result is consistent with existing reactor studies demonstrating that optimal particle diameters and Ar values correspond to cases with short-lived clusters, although more thorough experimental studies are needed.